leads4pass has updated Cisco 300-410 dumps issues! The latest 300-410 exam questions can help you pass the exam! All questions are corrected to ensure authenticity and effectiveness! Download the leads4pass 300-410 VCE dumps or PDF dumps: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html (Total Questions: 118 Q&A 300-410 Dumps)
Examsdemo Exam Table of Contents:
- Latest Cisco 300-410 google drive
- Effective Cisco 300-410 Practice testing questions
- leads4pass Year-round Discount Code
- What are the advantages of leads4pass?
Latest Cisco 300-410 google drive
[Latest PDF] Free Cisco 300-410 pdf dumps download from Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1lAE2gCoC-sXwaNu-CTVJJ1Z-IVv_TA-B/
Share Cisco 300-410 exam questions for free
QUESTION 1
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the SNMP attributes in Cisco IOS devices from the left onto the correct SNMPv2c or SNMPV3 categories
on the right.
Select and Place: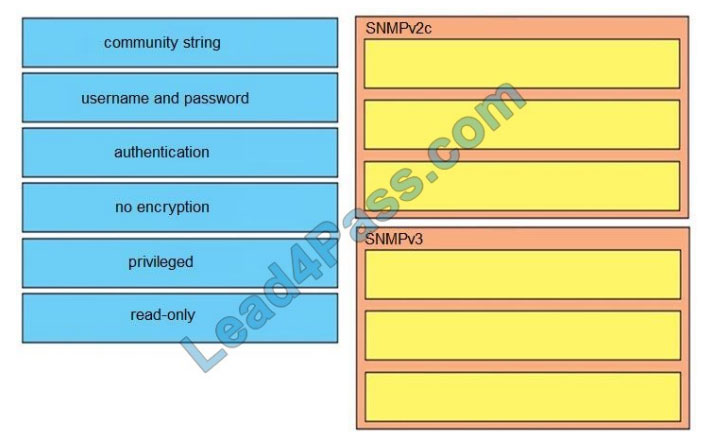
Correct Answer:
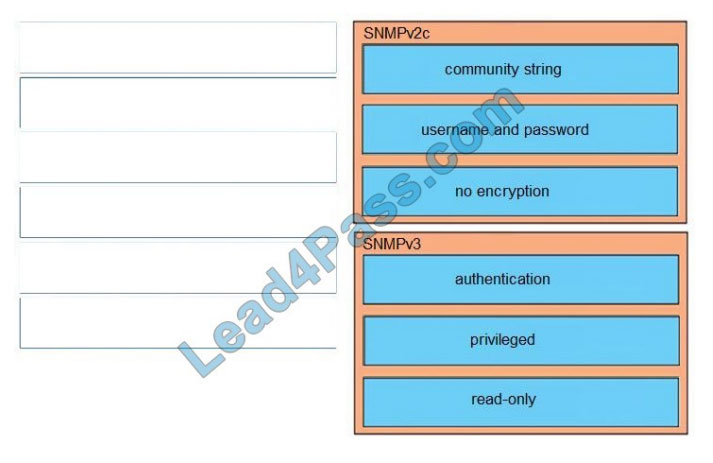
QUESTION 2
Which Cisco VPN technology can use the multipoint tunnel, resulting in a single GRE tunnel interface on the hub, to support
multiple connections from multiple spoke devices?
A. DMVPN
B. GETVPN
C. Cisco Easy VPN
D. FlexVPN
Correct Answer: A
QUESTION 3
Which next hop is going to be used for 172.17.1.0/24?
A. 10.0.0.1
B. 192.168.1.2
C. 10.0.0.2
D. 192.168.3.2
Correct Answer: A
QUESTION 4
Which label operations are performed by a label edge router?
A. SWAP and POP
B. SWAP and PUSH
C. PUSH and PHP
D. PUSH and POP
Correct Answer: D
A label edge router (LER, also known as edge LSR) is a router that operates at the edge of an MPLS network and acts
as the entry and exit points for the network. LERs push an MPLS label onto an incoming packet and pop it off an
outgoing
packet.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/sw/nxos/mpls/configuration/guide/mpls_cg/mp_mpls_overview.pdf
QUESTION 5
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the OSPF adjacency states from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
Select and Place: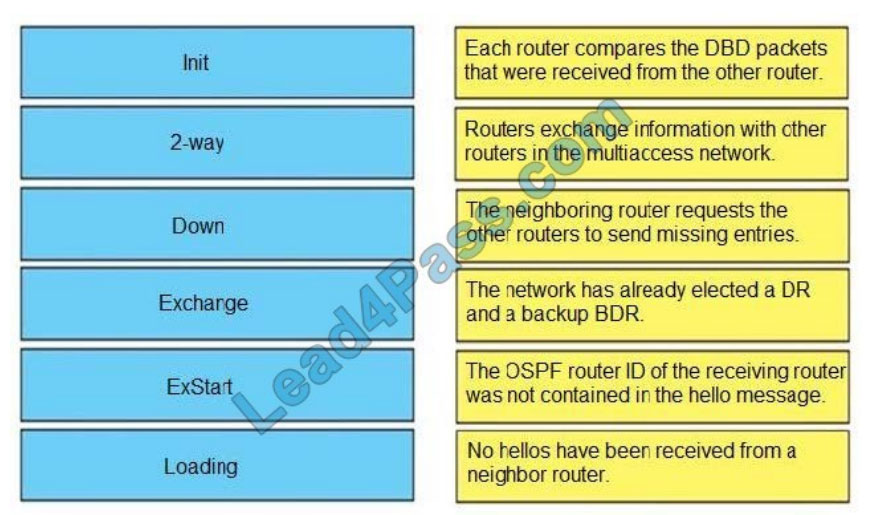
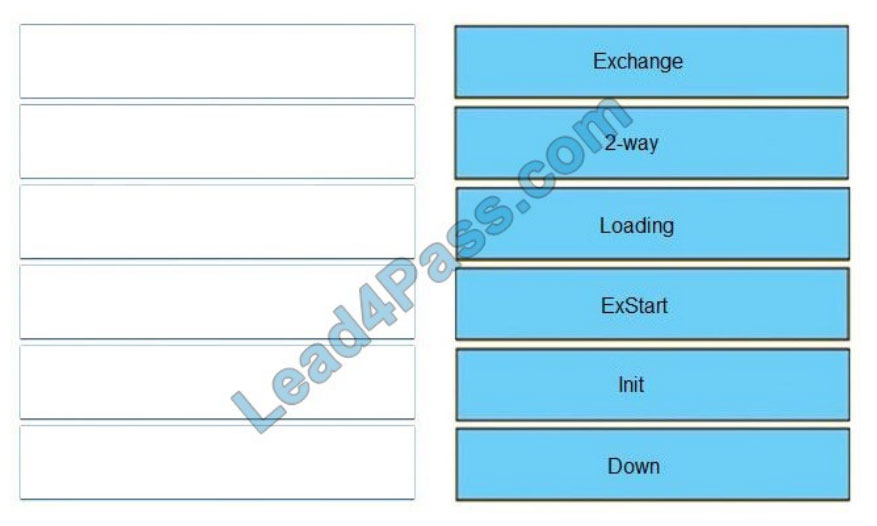
Correct Answer:

Down This is the first OSPF neighbor state. It means that no information (hellos) has been received from this neighbor,
but hello packets can still be sent to the neighbor in this state. During the fully adjacent neighbor state, if a router
doesn\\’t receive a hello packet from a neighbor within the Router Dead Interval time (RouterDeadInterval =
4*HelloInterval by default) or if the manually configured neighbor is being removed from the configuration, then the
neighbor state changes from Full to Down.
Attempt This state is only valid for manually configured neighbors in an NBMA environment. In an Attempt state, the router
sends unicast hello packets every poll interval to the neighbor, from which hellos have not been received within the
dead interval. Init This state specifies that the router has received a hello packet from its neighbor, but the receiving
router\\’s ID was not included in the Hello packet. When a router receives a hello packet from a neighbor, it should list
the sender\\’s router ID in its hello packet as an acknowledgment that it received a valid hello packet.
2-Way This state designates that bi-directional communication has been established between two routers. Bi-directional
means that each router has seen the other\\’s hello packet. This state is attained when the router receiving the hello
packet sees its own Router ID within the received hello packet\\’s neighbor field. At this state, a router decides whether
to become adjacent to this neighbor. On broadcast media and non-broadcast multiaccess networks, a router becomes
full only with the designated router (DR) and the backup designated router (BDR); it stays in the 2-way state with all
other neighbors. On Point-to-point and Point-to-multipoint networks, a router becomes full with all connected routers. At
the end of this stage, the DR and BDR for broadcast and non-broadcast multiaccess networks are elected. For more
information on the DR election process, refer to DR Election. Note: Receiving a Database Descriptor (DBD) packet from
a neighbor in the init state will also cause a transition to a 2-way state.
Exstart Once the DR and BDR are elected, the actual process of exchanging link-state information can start between
the routers and their DR and BDR. (ie. Shared or NBMA networks). In this state, the routers and their DR and BDR
establish a master-slave relationship and choose the initial sequence number for adjacency formation. The router with
the higher router ID becomes the master and starts the exchange, and as such, is the only router that can increment the
sequence number. Note that one would logically conclude that the DR/BDR with the highest router ID will become the
master during this process of master-slave relation. Remember that the DR/BDR election might be purely by virtue of a
higher priority configured on the router instead of the highest router ID. Thus, it is possible that DR plays the role of a slave.
And also note that the master/slave election is on a per-neighbor basis.
Exchange In the exchange state, OSPF routers exchange database descriptor (DBD) packets. Database descriptors
contain link-state advertisement (LSA) headers only and describe the contents of the entire link-state database. Each
DBD packet has a sequence number that can be incremented only by the master which is explicitly acknowledged by the slave. Routers also send link-state request packets and link-state update packets (which contain the entire LSA) in this
state. The contents of the DBD received are compared to the information contained in the routers link-state database to
check if new or more current link-state information is available with the neighbor.
Loading In this state, the actual exchange of link-state information occurs. Based on the information provided by the
DBDs, routers send link-state request packets. The neighbor then provides the requested link-state information in link state update packets. During the adjacency, if a router receives an outdated or missing LSA, it requests that LSA by
sending a link-state request packet. All link-state update packets are acknowledged.
Full In this state, routers are fully adjacent to each other. All the router and network LSAs are exchanged and the
routers\\’ databases are fully synchronized. Full is the normal state for an OSPF router. If a router is stuck in another
state, it is an indication that there are problems in forming adjacencies. The only exception to this is the 2-way state,
which is normal in a broadcast network. Routers achieve the FULL state with their DR and BDR in NBMA/broadcast
media and FULL state with every neighbor in the remaining media such as point-to-point and point-to-multipoint. Note:
The DR and BDR that achieve a FULL state with every router on the segment will display FULL/BROTHER when you
enter the show IP OSPF neighbor command on either a DR or BDR. This simply means that the neighbor is not a DR or
BDR, but since the router on which the command was entered is either a DR or BDR, this shows the neighbor as
FULL/BROTHER.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/open-shortest-path-first-ospf/13685-13.html
+
Each router compares the DBD packets that were received from the other router: Exchange
+
Routers exchange information with other routers in the multiaccess network: Exstart
+
The neighboring router requests the other routers to send missing entries: Loading
+
The network has already elected a DR and a backup BDR: 2-way
+
The OSPF router ID of the receiving router was not contained in the hello message: Init
+
No hellos have been received from a neighbor router: Down
When OSPF adjacency is formed, a router goes through several state changes before it becomes fully adjacent with its
neighbor.
The states are Down -> Attempt (optional) -> Init -> 2-Way -> Exstart -> Exchange -> Loading -> Full. Short descriptions
about these states are listed below:
Down: no information (hellos) has been received from this neighbor. Attempt: only valid for manually configured
neighbors in an NBMA environment. In Attempt state, the router sends unicast hello packets every poll interval to the
neighbor,
from which hellos have not been received within the dead interval.
Init: specifies that the router has received a hello packet from its neighbor, but the receiving router\\’s ID was not
included in the hello packet
2-Way: indicates bi-directional communication has been established between two routers. Extract: Once the DR and
BDR is elected, the actual process of exchanging link-state information can start between the routers and their DR
and
BDR.
Exchange: OSPF routers exchange and compare database descriptor (DBD) packets Loading: In this state, the actual
exchange of link-state information occurs. Outdated or missing entries are also requested to be resent.
Full: routers are fully adjacent with each other
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk365/technologies_tech_note09186a0080093f0e.shtml
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/open-shortest-path-first-ospf/13685-13.html Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/open-shortest-path-first-ospf/13685-13.html
QUESTION 6
Refer to the exhibit. A network engineer executes the show ipv6 OSPF database command and is presented with the
output that is shown. Which flooding scope is referenced in the link-state type?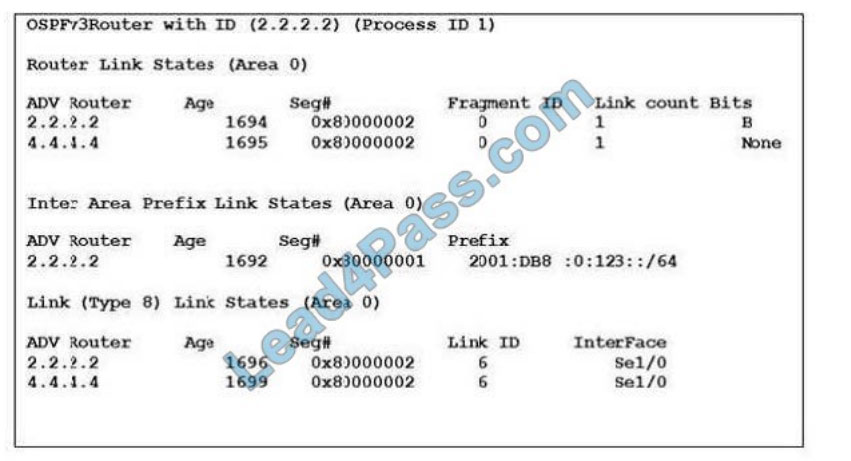
A. link-local
B. area
C. As (OSPF domain)
D. reserved
Correct Answer: B
QUESTION 7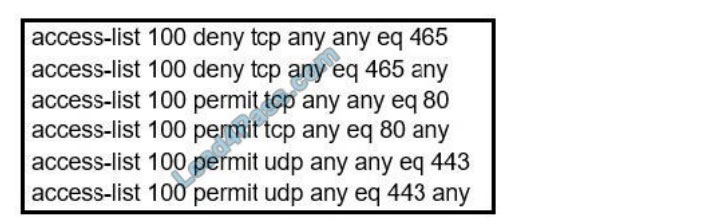
Refer to the exhibit. During troubleshooting, it was discovered that the device is not reachable using a secure web
browser. What is needed to fix the problem?
A. permit TCP port 443
B. permit UDP port 465
C. permit TCP port 465
D. permit TCP port 22
Correct Answer: A
QUESTION 8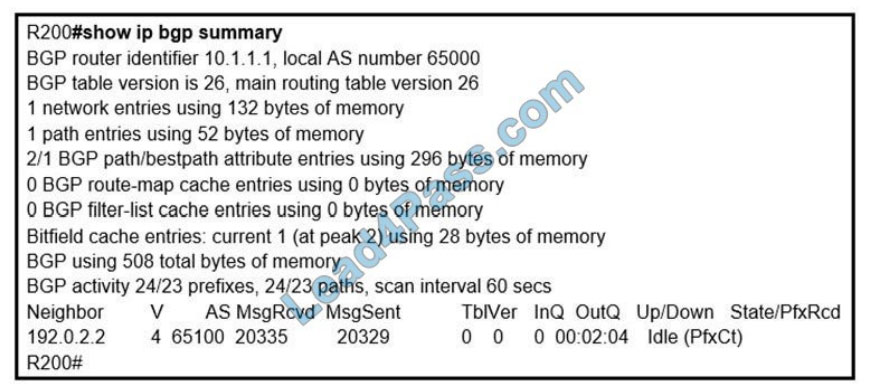
Refer to the exhibit. In which circumstance does the BGP neighbor remain in the idle condition?
A. if prefixes are not received from the BGP peer
B. if prefixes reach the maximum limit
C. if a prefix list is applied in the inbound direction
D. if prefixes exceed the maximum limit
Correct Answer: D
QUESTION 9
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is trying to block the route to 192.168.2.2 from the routing table by using the
configuration that is shown. The route is still present in the routing table as an OSPF route. Which action blocks the
route?
A. Use an extended access list instead of a standard access list.
B. Change sequence 10 in the route-map command from permit to deny.
C. Use a prefix-list instead of an access list in the route map.
D. Add this statement to the route map: route-map RM-OSPF-DL denies 20.
Correct Answer: C
QUESTION 10
While working with software images, an engineer observes that Cisco DNA Center cannot upload its software image
directly from the device. Why is the image not uploading?
A. The device must be resynced to Cisco DNA Center.
B. The software image for the device is in install mode.
C. The device has lost connectivity to Cisco DNA Center.
D. The software image for the device is in bundle mode
Correct Answer: B
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/cloud-systems-management/network-automation-and/management/dna-center/1-2-10/user_guide/b_cisco_dna_center_ug_1_2_10/b_dnac_ug_1_2_10_chapter_0100.html
QUESTION 11
Refer to the exhibit.
A company is evaluating multiple network management system tools. Trending graphs generated by SNMP data are
returned by the NMS and appear to have multiple gaps. While troubleshooting the issue, an engineer noticed the
relevant output.
What solves the gaps in the graphs?
A. Remove the exceed-rate command in the class map.
B. Remove the class-map NMS from being part of control plane policing.
C. Configure the CIR rate to a lower value that accommodates all the NMS tools
D. Separate the NMS class-map into multiple class maps based on the specific protocols with appropriate CoPP actions
Correct Answer: D
Reference: https://tools.cisco.com/security/center/resources/copp_best_practices
QUESTION 12
Refer to the following output:
Router#show ip nhrp detail
1.1.2/8 via 10.2.1.2, Tunnel1 created 00:00:12, expire 01:59:47 TypE. dynamic, Flags: authoritative unique nat
registered used NBMA address:
10.12.1.2
What does the authoritative flag mean in regards to the NHRP information?
A. It was obtained directly from the next-hop server.
B. Data packets are process switches for this mapping entry.
C. NHRP mapping is for networks that are local to this router.
D. The mapping entry was created in response to an NHRP registration request.
E. The NHRP mapping entry cannot be overwritten
Correct Answer: A
QUESTION 13
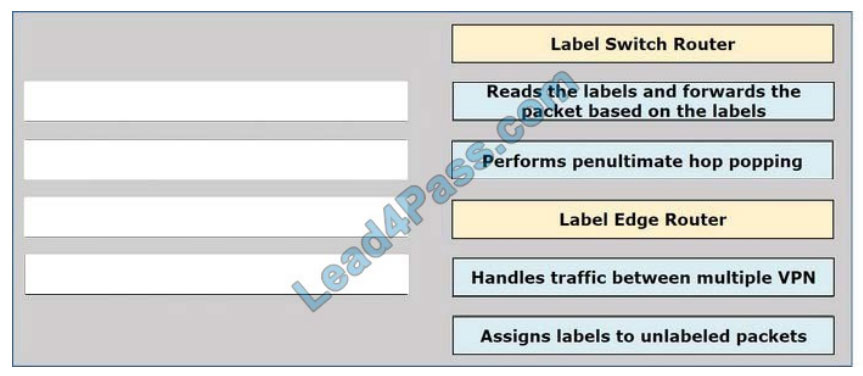
Drag and drop the operations from the left onto the locations where the operations are performed on the right. Drag
each definition on the left to the matching term on the right.
Select and Place: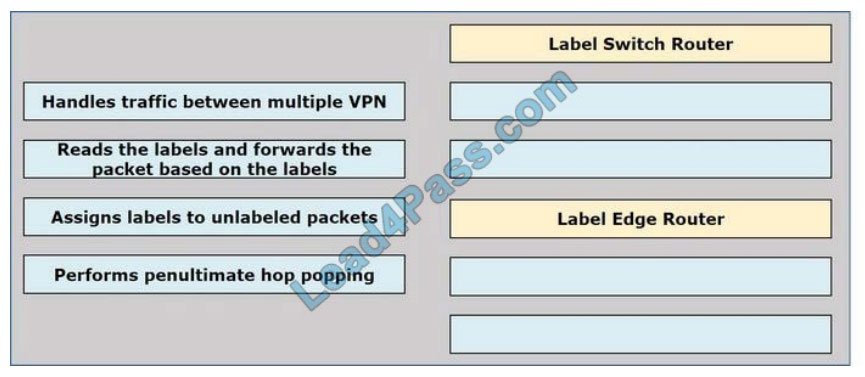
Correct Answer:
Latest leads4pass Cisco dumps Discount Code 2020

About The leads4pass Dumps Advantage
leads4pass has 7 years of exam experience! A number of professional Cisco exam experts! Update exam questions throughout the year! The most complete exam questions and answers! The safest buying experience! The greatest free sharing of exam practice questions and answers!
Our goal is to help more people pass the Cisco exam! Exams are a part of life, but they are important! In the study, you need to sum up the study! Trust leads4pass to help you pass the exam 100%!
Summarize:
This blog shares the latest Cisco 300-410 exam dumps, 300-410 exam questions and answers! 300-410 pdf, 300-410 exam video!
You can also practice the test online! leads4pass is the industry leader!
Select leads4pass 300-410 exams Pass Cisco 300-410 exams “Implementing Cisco Enterprise Advanced Routing and Services (ENARSI)”. Help you successfully pass the 300-410 exam.
ps.
Get Cisco Full Series Exam Dumps: https://www.fulldumps.com/?s=Cisco (Updated daily)
Get leads4pass Cisco CCNP exam dumps: https://www.leads4pass.com/ccnp.html
Latest update leads4pass 300-410 exam dumps: https://www.leads4pass.com/300-410.html (118 Q&As)
[Q1-Q12 PDF] Free Cisco 300-410 pdf dumps download from Google Drive: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1lAE2gCoC-sXwaNu-CTVJJ1Z-IVv_TA-B/